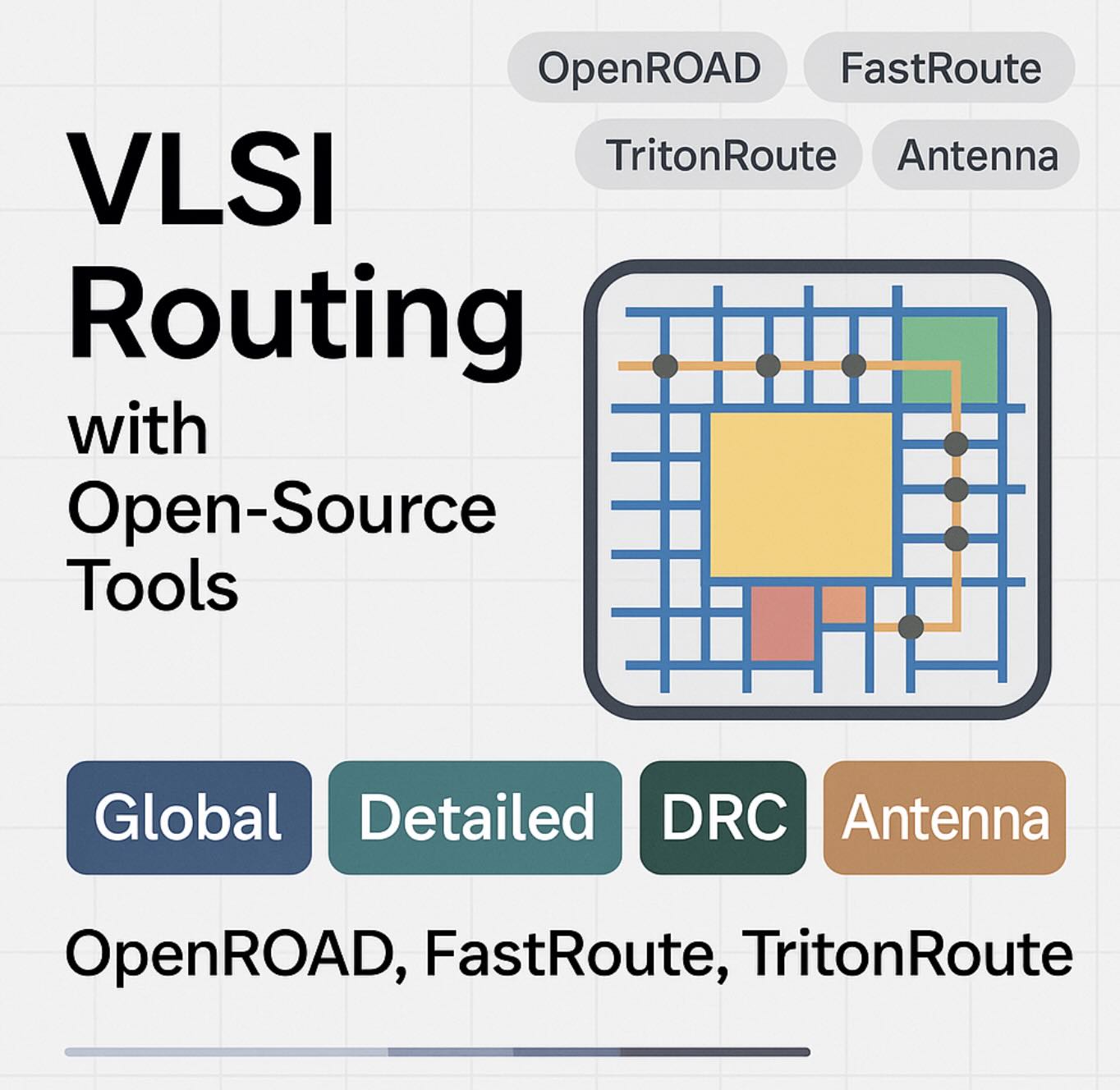
Introduction
Routing connects all pins and nets on metal layers while honoring design rules and timing. In the open-source stack, FastRoute plans coarse paths (global routing) and TritonRoute commits exact wires/vias (detailed routing). This guide shows how to configure layers, manage congestion, repair antenna, and iterate with STA to close timing.
Routing flow at a glance
- Prep: set allowed layers, preferred directions, blockages/keep-outs, NDRs, shields.
- Global route: guide edges across a grid; detect hotspots; tweak costs.
- Detailed route: lay tracks & vias; fix shorts/spacings; finish.
- Antenna repair: auto-insert diodes/jumpers for long unfinished nets.
- DRC cleanup: resolve remaining min-width/spacing/via/metal density issues.
- Extract & analyze: RC parasitics → STA → ECO (buffers/sizing/re-route).
Prep: layers, constraints & blockages
Choose layers and protect sensitive regions before you route.
# Load tech/lib views (sky130 example paths abbreviated)
read_lef tech.tlef
read_lef sky130_fd_sc_hd__merged.lef
read_def placed.def
# Allow routing from M1..M5 (example)
set_routing_layers -signal met1-met5 -clock met3-met5
# Preferred directions usually: M1 horiz, M2 vert, ...
# (Provided in tech LEF; override with:)
set_preferred_routing_direction met2 vertical
set_preferred_routing_direction met3 horizontal
# Place a routing blockage (keep-out) over an analog macro
add_routing_blockage -rects "120 80 220 160" -layers met2-met4 -type hard
# Create a non-default rule (NDR) for critical clock nets (wider wires / larger spacing)
create_ndr -name CLK_NDR -width_multiplier 2.0 -spacing_multiplier 2.0 -layers met3-met5
set_net_routing_rules -nets {clk} -ndr CLK_NDR
# Optional shielding for a noisy net
set_shielding -nets {serdes_tx} -shield_net VSS -layers met4-met5
Tip: Use minimal layers for small blocks to reduce vias; add upper layers when congestion appears.
Global routing (FastRoute)
Global routing estimates paths on a coarse grid and generates guides for detailed routing. You’ll tune costs to reduce overflow (congestion).
# Congestion-driven global routing
global_route -congestion_iterations 30 -allow_congestion
# Export route guides for TritonRoute
write_guides design.guide
# Visual checks
report_congestion -global
write_congestion_map congestion.rpt
- Overflow > 0 means demand exceeds capacity on some edges—reduce utilization or open more layers.
- Blockages near macros often cause hot stripes—widen channels or move pins.
Detailed routing (TritonRoute)
TritonRoute uses the guides to assign exact tracks, drop vias, and iterate DRC repair. It reports violations as it routes.
# Use previously written guides
detailed_route -output_drc drc.rpt -via_in_pin_bottom_layer_cut_spacing
# Optional: incremental fix after small ECOs
detailed_route -incremental -output_drc drc_inc.rpt
# Exports
write_def routed.def
write_gds routed.gds
If DRCs explode, relax some constraints, add a layer, or reduce utilization and try again.
Antenna repair
Long wires connected to transistor gates can accumulate charge during fabrication. Use automated diode insertion or “jumpers” (early vias to higher metal) to fix antenna violations.
# Analyze antenna after detailed route
check_antenna -report antenna.rpt
# Repair using library diodes (ensure diode cells are available in the LEF/Liberty)
repair_antenna -max_fixes 1000 -iterations 3
write_def routed_antenna.def
DRC cleanup & common violations
- Short/Spacing: relax guides, widen channels, route critical nets first.
- Min-width/min-area: enforce minimum jog/patch; TritonRoute can auto-patch small segments.
- Via rules: try alternative via types or allow stacked vias where legal.
- End-of-line: avoid acute jogs near parallel edges; increase EOL spacing.
magic -T sky130A.tech
# Inside Magic:
gds read routed.gds
load top
drc check
drc find
RC extraction & timing closure loop
After routing, extract parasitics and re-run STA. Use ECOs (buffer/sizing/upsizing NDR/shielding) and, if needed, incremental re-route on the worst paths.
# Extract RC (OpenROAD's built-in extraction)
estimate_parasitics -global_routing
write_spef design.spef
# Timing with OpenSTA
read_liberty sky130_fd_sc_hd__tt_025C_1v80.lib
read_verilog routed_netlist.v
read_sdc design.sdc
read_spef design.spef
link_design top
report_checks -path_delay min_max -fields {cap slew} -digits 3 > timing_after_route.rpt
Loop: fix worst negative slack (WNS/TNS) via buffering/sizing → incremental route → re-extract → STA.
Best practices & debugging
- Keep clock nets on robust upper metals with NDRs; shield if jitter-sensitive.
- Pin access matters: rotate/move cells or update pin shapes to avoid detours.
- Prefer fewer jogs; straight, layer-appropriate routes reduce RC.
- When congestion persists: open one more metal layer or reduce placement density 2–5%.
- Version all route logs and DRC/antenna/timing reports for reproducibility.
FAQ
Which layers should signals use? Lower metals for local, mid metals for data buses, upper metals for long/clock nets.
Do I route before antenna repair? Yes—detailed route first, then analyze and repair antenna.
How do I push one net first? Create a route group or raise its priority; some flows support rip-up & re-route on target nets.
You might also like